Our interaction with the natural environment
Water and Effluents
Neo’s Water Strategy
Neo recognizes water withdrawal and discharge can significantly impact the environment and contribute to our environmental footprint. Water management risks related to withdrawals, consumption, and discharge such as depletion of water resources, negative impacts on aquatic ecosystems, and contamination of water sources are thoroughly evaluated by Neo’s plant operations teams. Our manufacturing facilities commonly use water for feedstock processing and cooling. Wastewater treatment is performed either on-site or through a wastewater treatment service. Seawater accounts for over 50% of the water withdrawn from our plants, with surface water, ground water, and utility-sourced water making up the remaining portion.
Water Withdrawal
Neo’s total water withdrawal in 2022 is 2.325 million cubic meters (m3).
- Four of our ten primary operating facilities are located in regions classified as either High or Extremely High Water Baseline Water Stress levels according to the World Resource Institute’s (WRI) Water Risk Atlas tool, “Aqueduct.” These facilities’ water withdrawal represents 76% of Neo’s total water withdrawn, excluding seawater withdrawal.
- 59% of our water withdrawal is sourced from the Baltic Sea’s Gulf of Finland, and is primarily used for cooling purposes. This water is returned to the sea without the need for any chemical treatment.
- In 2022, our total water discharge amounted to 2.199 million cubic meters, which represents 94.6% of our total water withdrawn.
- 92% of all water withdrawn is returned to its source.Total water consumption in 2021 was 896 thousand cubic meters; 696 thousand cubic meters was consumed in high stress water regions, or 78% of water consumed. Water consumption is defined as water that is either evaporated, incorporated into our products, or is otherwise not returned to the same origin source. As much of our water dispersed comes from surface water or utilities and is ultimately dispersed in the sea, this water dispersal does not reduce our reported water consumption.
Neo evaluates water consumption as water that is not returned to the same source, either due to evaporation, incorporation into products, or other reasons. In 2022, the total water consumption amounted to 301 thousand cubic meters, of which 277 thousand cubic meters were consumed in regions with high water stress, accounting for 92% of the water consumed.
On a pro-rata basis, Neo’s net change in water withdrawn versus water discharged across all production represents less than 1 percent of a cubic meter of water consumed per kilogram of material produced. This is equivalent to about 9 liters of water for every kilogram of product manufactured. Our manufacturing operations are designed to incorporate water usage based upon the processing needs and availability of local water resources. Managing water withdrawal, consumption, and discharge is regular practice across all of our plants. Neo strives to meet and/ or exceed all water discharge quality laws and regulations mandated by host jurisdictions. In 2022, Neo had zero (0) incidents of non-compliance associated with water quality permits, standards, and regulations.
Neo’s manufacturing operations are designed to utilize water resources efficiently, taking into account the specific processing requirements and the availability of local water sources. We have a regular practice of managing water withdrawal, consumption, and discharge in all of our plants.
Water Saving at Neo
Neo’s production plants across the globe continues to find innovative and creative solutions to reduce water usage/consumption and impact from water discharge. In 2022, water related initiatives and projects include:
- Our Tianjin, China facility utilizes a rainwater collection system. Collecting 1,000 tons of water per year used toward watering lawns and vegetations.
- Our Tianjin, China facility implemented cooling water recycling system, reducing water withdrawal and discharge by 24,000 tons per year.
- Our Zibo, China facility re-uses its cleaning water, saving 11,000 m3 of water withdrawal and discharge per year.
- Our Zibo, China facility collects and uses process condensate for its rare earths production, saving 31,935 m3 of process water per year.
- Our Korat, Thailand facility has on-site water treatment capabilities. Recycled water is used to water vegetation.
- Our Sillamäe, Estonia facility rebuilt part of the niobium EBMs cooling loops, which increases cooling efficiency and reduced sea water usage/withdrawal by two times.



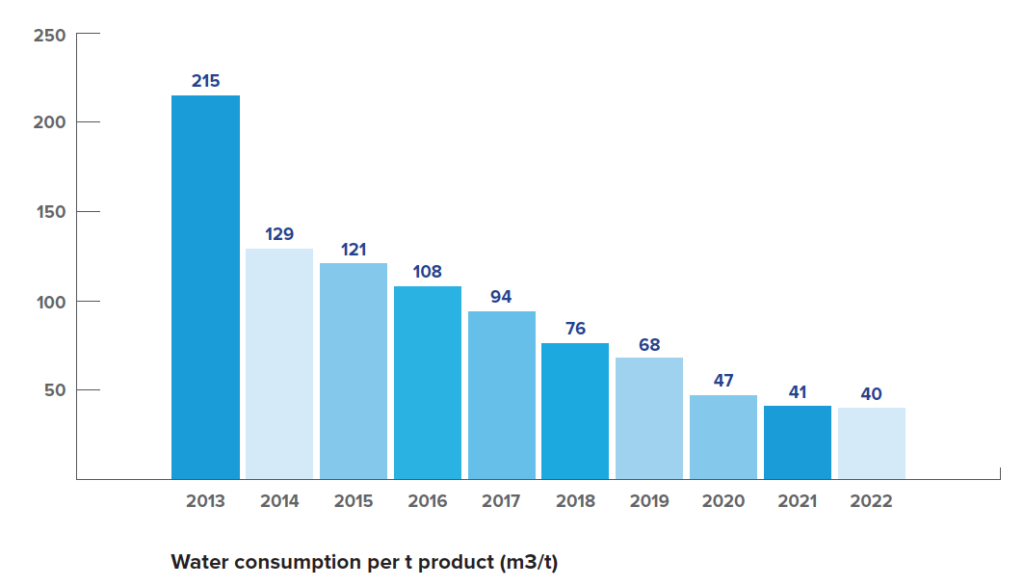
Water Savings: A Case Study
High Water Stress Regions
Four of our plants operate in high or Extremely High Water Stress Regions: Sillamäe, Estonia; Sagard, Germany (de minimis water consumption); Tianjin, China; and Zibo, China.
Sillamäe
Sillamäe, Estonia is home to facilities associated with both Neo’s Rare Metals and Chemicals and Oxides business units. This site accounts for 75% of the company’s total water withdrawn. However, 79% of Sillamäe’s water withdrawal comes from the Baltic Sea. The site’s actual water withdrawal is 375 thousand cubic meters, and the net change between water withdrawn and discharged is 82 thousand cubic meters. Sillamäe’s facilities are situated adjacent to the Gulf of Finland and Stoke River. The site closely monitors the quantity and quality of its water and effluents. Sillamäe has reported through its Environmental Impact Assessment that the site’s production activities do not have a negative impact on the water quality on nearby water bodies within the impact area. Water recycling systems are among some of the water-saving and impact reduction strategies frequently employed at the site.
Sagard
Our Sagard, Germany facility is located in a high water stress region, although it withdraws and discharges a de minimis amount of water. Management views this as a low-risk water resource operation.
Zibo
Our Zibo (China) plant operates in a high water stress region. The plant has routinely invested in upgrades to its wastewater treatment and pre-treatment discharge systems to exceed local environmental emissions regulations. In 2022, Zibo withdrew 239 thousand metric tons of water, and discharged 208 thousand metric tons of water. Total water consumption was 31 thousand metric tons. Given that our plant location is within a chemical and industrial park that overlaps with the municipal’s primary water source—a ground watershed area known as Dawu–there is heightened interest in protecting this groundwater source from potential surface pollution. This renewed concern is in light of current Municipal Government plans for continued growth in Zibo City, and in review of a historic oil spill by a neighboring petrochemical company in the mid-1980s. Local plant management has been supportive of these efforts to help alleviate potential risks of groundwater contamination. As a result, Neo is joining many of the industrial plants in this community to relocate to a new industrial zone, located a safe distance from the primary recharging areas of this unique groundwater system. The new industrial park will also offer new and upgraded water and wastewater treatment infrastructure. In 2021, we made substantial progress on the site choice and engineering design for the soon to be modernized and upgraded manufacturing facility. The plant was awarded “Excellence in Major Construction Project” by the local government in recognition of the plant’s relocation project in 2022.
Tianjin
Our plant at Tianjin (China) is located in an Extremely High water stress region, although it is in close proximity to low stress regions (less than 10 kilometers from the plant). It primarily sources water from municipal supply, collects and uses rainwater for watering its surrounding flora ecosystem, and deploys water recycling for industrial cooling. In 2022 it withdrew and consumed 106 thousand cubic meters of water, and it discharged 106 thousand cubic meters of water. It’s discharge as a percent of water withdrawn rate is 100%.
In 2016, the Tianjin facility was awarded the title of “Water-Saving Enterprise of Tianjin” and has continued to reduce its water usage by over 10% in subsequent years. This accomplishment can be attributed in part to the installation of a network of water meters and sensors, which allows for the rapid identification and isolation of any water repair issues. The plant also established an advanced treatment station in 2019 to treat electrophoresis wastewater and is in compliance with local regulations, discharging at Level III standard. Quarterly assessment of discharge water is conducted to ensure discharge quality meets and exceeds minimum compliance requirement.
We prioritize addressing water intensity issues at all of our plants, and the local management at each plant assesses and controls these risks. At Neo’s Peterborough plant, for example, water consumption and wastewater per kilogram of gallium and indium processed have been reduced by over 50% in the past decade.
